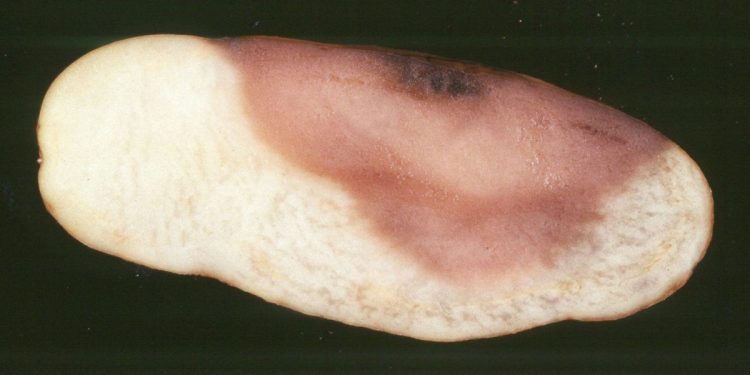
: This article focuses on the devastating plant disease known as pink rot, caused by Phytophthora erythroseptica, which poses a significant threat to potato crops globally. We will delve into the latest data on the disease, including its development and the consequences it can have on potato crops. Furthermore, we will provide strategies for farmers, agronomists, and agricultural engineers to prevent the spread of pink rot in their potato crops.
Pink rot caused by Phytophthora erythroseptica is a severe disease that affects potato crops worldwide. According to recent data from the University of Minnesota, pink rot can cause yield losses of up to 60%, leading to significant financial losses for farmers. The disease is prevalent in areas with high soil moisture and warm temperatures, making it a significant concern for potato farmers worldwide.
The development of pink rot is influenced by various factors such as soil type, irrigation practices, and temperature. The fungus can enter the potato plant through the roots and move upward through the stem, eventually causing extensive damage to the potato. Recent research has shown that implementing good crop management practices such as using pathogen-free seed potatoes, avoiding over-irrigation, and timely harvesting can help prevent the spread of pink rot in potato crops.
In conclusion, pink rot poses a severe threat to potato crops globally, leading to significant financial losses for farmers. It is crucial for farmers, agronomists, and agricultural engineers to work together to implement effective management strategies to prevent the spread of pink rot and minimize its impact on potato yields and quality.
#PinkRot #PhytophthoraErythroseptica #PotatoCrops #CropManagement #DiseasePrevention #PotatoVarieties #AgricultureResearch #Farmers #Agronomists #AgriculturalEngineers