#potatopower #sustainablefarming #nutritiouscrop
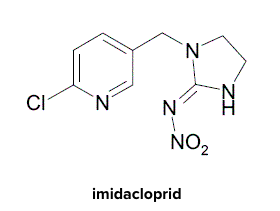
Potatoes are a versatile and nutritious crop that have been cultivated for thousands of years. With their ability to grow in a variety of climates and soil types, they have become a staple food for many people around the world. In recent years, the potato has also become an important crop for sustainable agriculture, thanks to its low environmental impact and high nutritional value. However, the potato crop is also vulnerable to pests and diseases, which can reduce yields and quality. One active substance that has been used to protect potatoes from pests is imidacloprid, which has both benefits and potential consequences for potato production.
Development: The potato, or Solanum tuberosum, is a member of the nightshade family and is native to the Andes region of South America. It was introduced to Europe in the 16th century and quickly became a popular food crop. Today, potatoes are grown in many parts of the world and are one of the most important crops for global food security.
Potatoes are rich in vitamins and minerals, such as vitamin C, potassium, and iron, and are also a good source of dietary fiber. They can be cooked in a variety of ways, such as boiled, mashed, fried, or baked, and are a popular ingredient in many dishes.
In recent years, the potato has become an important crop for sustainable agriculture, thanks to its ability to grow in a variety of climates and soil types. Potatoes are also low-input crops, meaning that they require relatively few resources, such as water and fertilizer, compared to other crops. Additionally, potatoes can be stored for long periods of time without spoiling, making them an ideal crop for food security.
However, potato crops are vulnerable to pests and diseases, which can reduce yields and quality. One active substance that has been used to protect potatoes from pests is imidacloprid. Imidacloprid is a systemic insecticide that is applied to the soil or foliage of potato plants. It is effective against a wide range of insect pests, such as aphids, whiteflies, and thrips, and can also have some fungicidal properties.
While imidacloprid can help protect potato crops from pests and diseases, there are also potential consequences to its use. Imidacloprid has been shown to be toxic to bees and other pollinators, which can have negative impacts on the environment and agricultural biodiversity. Additionally, there is some concern about the potential for imidacloprid to accumulate in the soil and water over time, which can have negative impacts on human health.
Consequences: The use of imidacloprid in potato production highlights the importance of responsible pesticide use and the need for sustainable agricultural practices. While pesticides can be an important tool for protecting crops, they must be used carefully and responsibly to avoid negative impacts on the environment and human health. In the case of imidacloprid, alternative pest management strategies, such as crop rotation and integrated pest management, may be more sustainable and effective in the long term.