The breeding is just not the “act” of crossing.
To start a breeding program it’s necessary to clearly establish the target market, then have a genetic base with good data, develop field tests and use tools to collect informations, have a seed program, and conduct market tests.
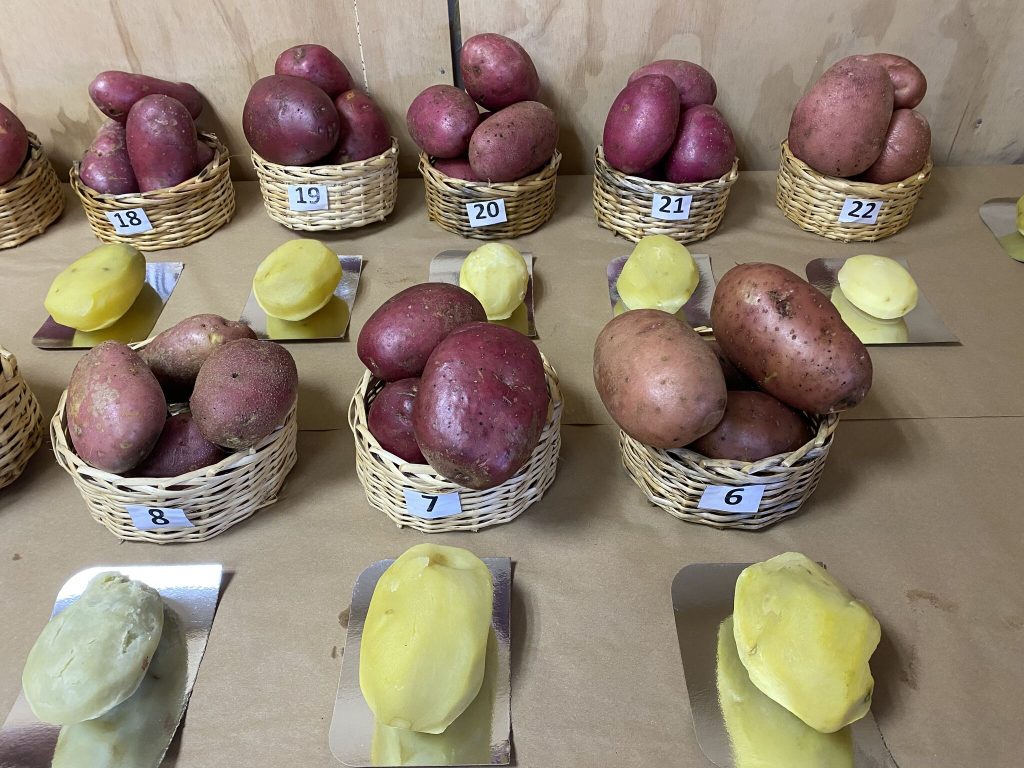
A) Market definition: each target market has clear needs, so they can be summarized as follows:
1. Main characteristics: Yield, quality, shape, skin finish, dry matter, maturity.
2. Second characteristics : ecogeographic growing area, skin diseases, nematodes resistance, storage diseases, bruising resistance,
3. Third characteristics : viral diseases , foliar diseases , sustainability.
4. Others: more specific for each target market
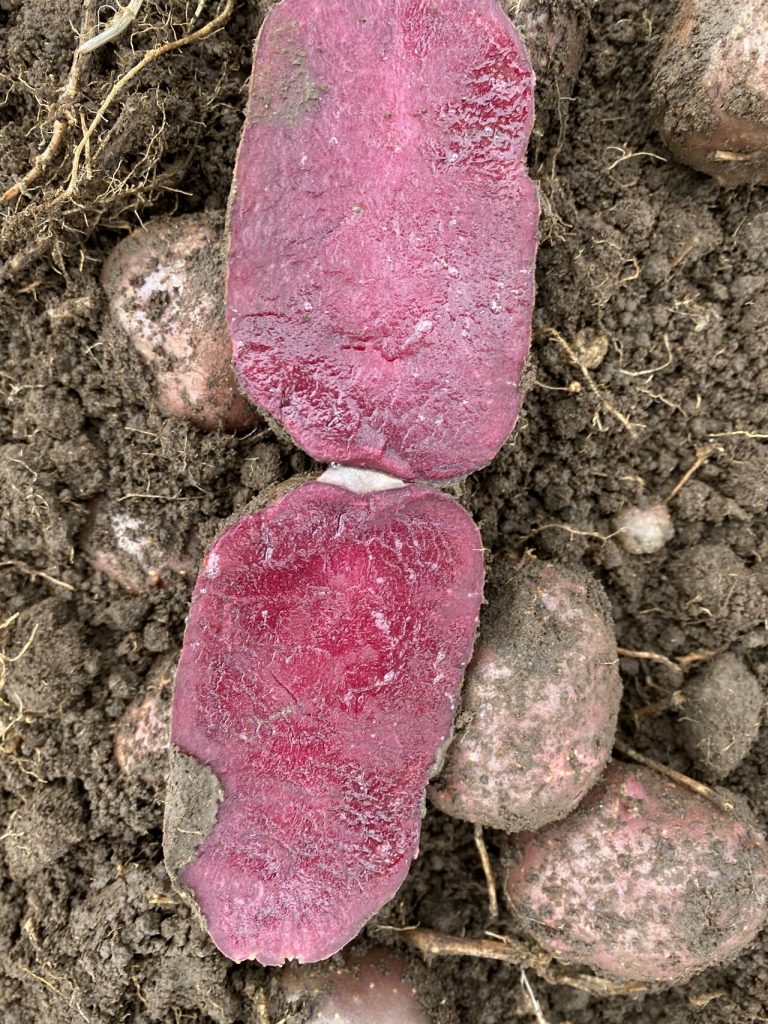
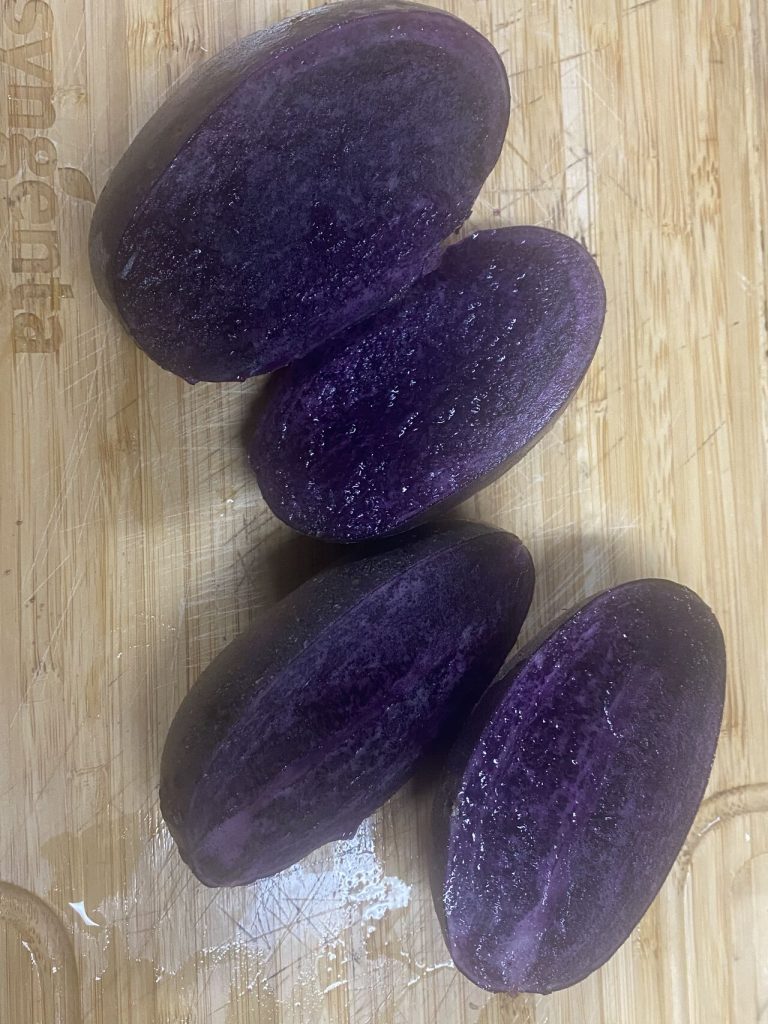
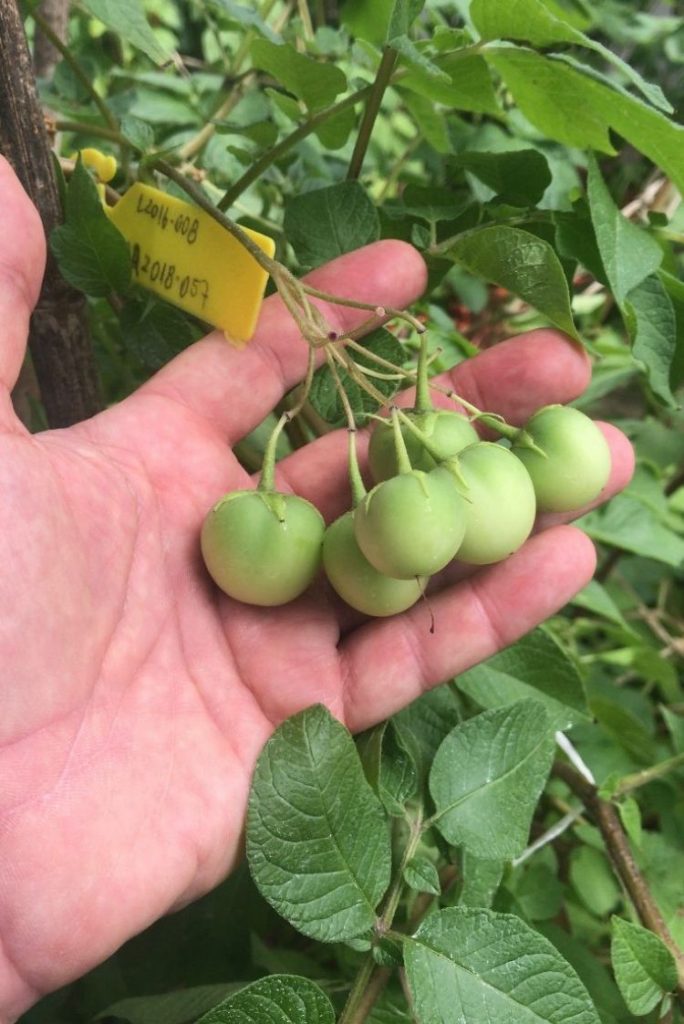
B) Genetic Base: can introduce or can use local varieties in production. In any case recording data under various conditions it’s the key to safe time. With this information the objetive is to add better characteristics (genes) to the new lines. And define clearly what NOT to accept.
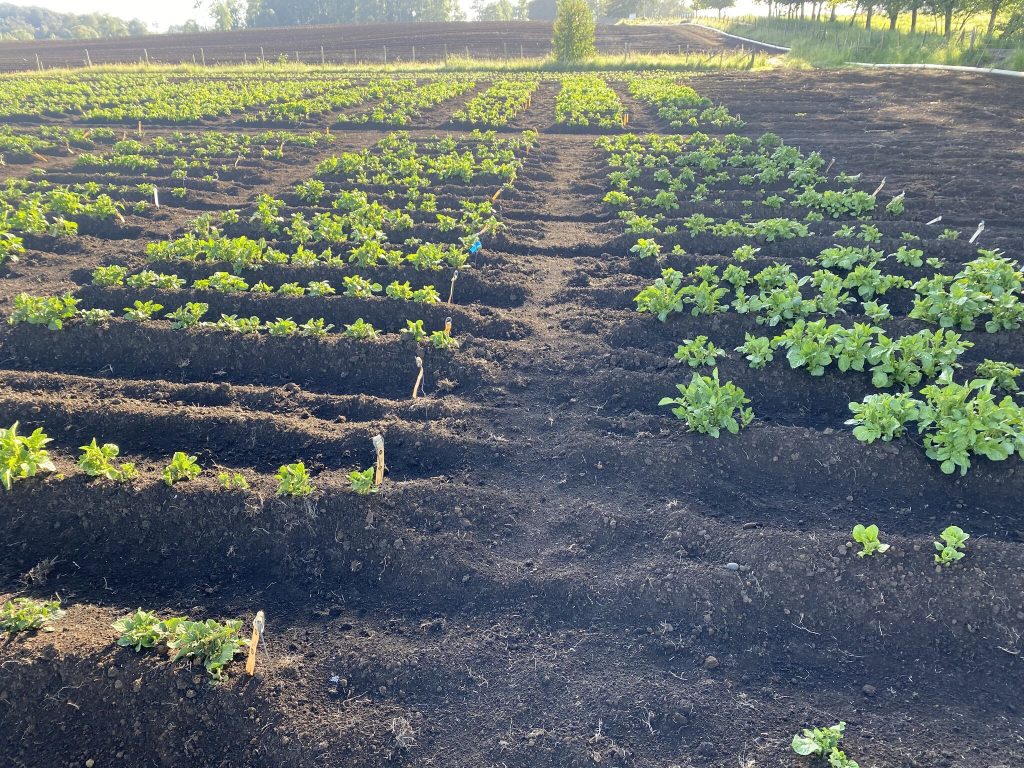
C) Trial fields: having a lot of data without practical tests and for several years and diferentes production areas can bring big problems in the future. That is why the creation of clear trial fields and destruction tests its so important. Data collection using tools like Molecular Markers is very useful in accelerating responses, but practical confirmatory testing is still necessary.
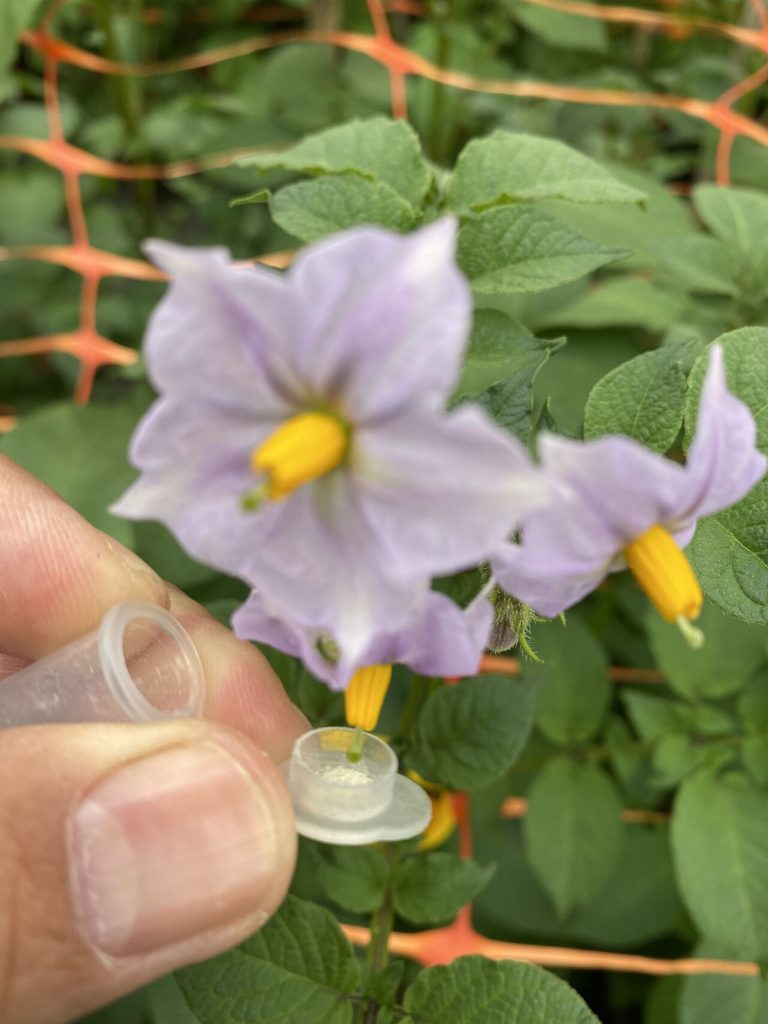
*mutagenesis , cisgenesis, crisper/cas/ speed breeding, molecular markers, dihaplois , are complementary tools or technics.
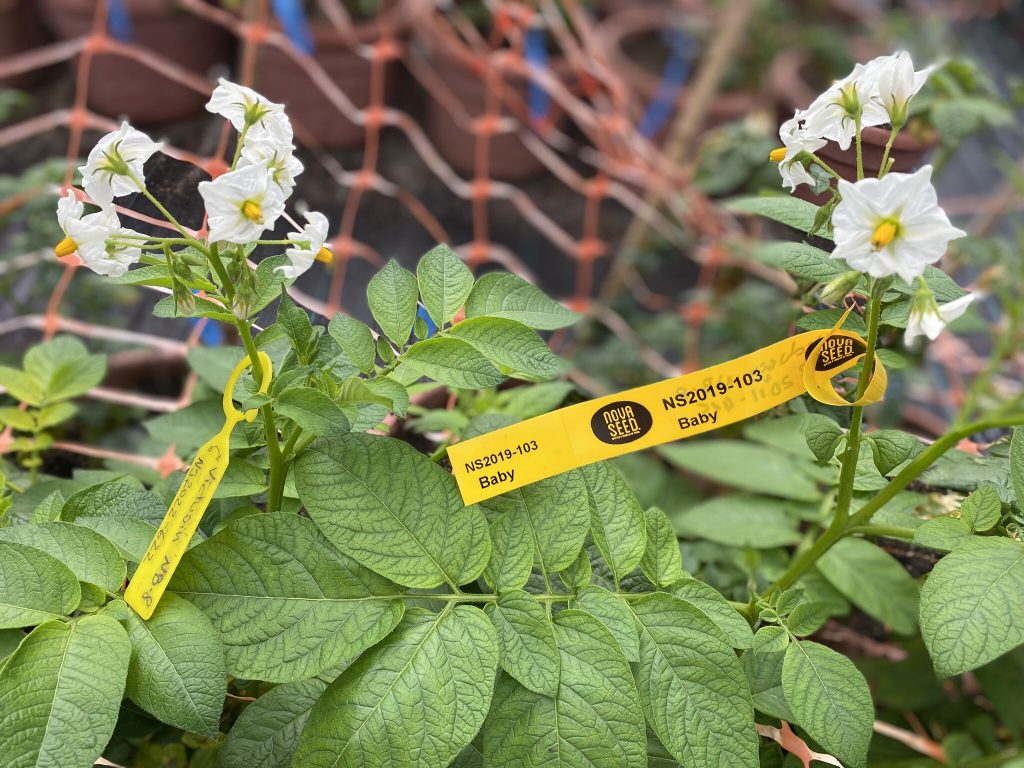
D) Seed production: once the selection is made, the seed program plays an important role. Without this program it can’t be tested at client level.
E) Market: the target market will test in quality and will decide whether to take or use the product again or not
This complete process takes more than 10 years. And each year an overview is needed to look for “future” needs/problems and make some corrections to the larger improvement program.