The foliage of potato plants can be damaged by herbicides applied to the crop, herbicides drifting over from neighbouring fields or herbicide residues that carry
over from a previous crop. Distorted plant growth and yellowing are typical symptoms of herbicide injury.
Laboratory analyses of soil, water, tubers or foliage are necessary to confirm herbicide damage.

Glyphosate
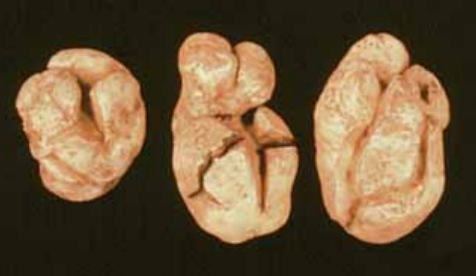
The drift of glyphosate onto potato foliage injures the crop. Tubers develop folds or clefts.

Phenoxy Herbicides
2,4 D and Dicamba injuries are caused by spray drift.
Picloram injury results from residue in the soil carried over from a previous crop.



Metribuzin
Metribuzin injury is more likely when the herbicide is applied after emergence. Metribuzin may injure potato plants when high rates are used, when it is applied to
sensitive varieties (e.g., Atlantic, CalWhite), or when the weather is cloudy, cool and wet before or soon after application.
Leaves turn yellow either along or between the veins, depending on the variety. If the injury is slight, the yellow tissue eventually becomes green.



Atrazine

EPTC
Potato foliage may be injured if applications of EPTC exceed recommended rates or if applications overlap during soil preparation before planting.

Linuron





Imazethapyr