Techniques of Potato Farming, Planting Methods, Harvesting
Today, we discuss the topic of potato farming techniques, tips, and ideas. This article also covers the plant care of potato and harvesting tips.
The Soil type is Suitable for Potato Plantation:

Potatoes will grow in just about any well-drained soil, but they dislike soggy soil. Because they do all their growing underground, they can expand more easily in loose, loamy soil than in heavy, compacted, clay soil that keeps plant roots from getting the air and water they need.
Best Planting or Sowing Time of Potato:

To secure high yields, it is essential to plant the potatoes at an optimum time. The best time of planting is when the maximum and minimum temperatures are from 30°C to 32°C and 18°C to 20°C, respectively; The planting period for different potato growing regions is given.
- Plant seed potatoes (pieces of the whole potato or a small whole potato, with at least 2 eyes per piece) 0-2 weeks after last spring frost.
- If you are cutting up potato pieces for planting, do so 1-2 days ahead of time. This will give them the chance to form a protective layer, both for moisture retention and rot resistance.
- You may start planting earlier, as soon as soil can be worked, but be aware that some crops will be ruined by a frost.
- Spread and mix in rotted manure or organic compost in the bottom of the trench before planting.
- Plant seed potatoes one foot apart in a 4-inch deep trench, eye side up.
- Potatoes are best grown in rows. To begin with, dig a trench that is 6-8 inches deep. Plant each piece of potato (cut side down, with the eyes pointing up) every 12-15 inches, with the rows spaced 3 feet apart. If your space is limited or if you would like to grow only baby potatoes, you can decrease the spacing between plants. To begin with only fill the trench in with 4 inches of soil. Let the plants start to grow and then continue to fill in the trench and even mound the soil around the plants as they continue to grow. Prior to planting, always make sure to cultivate the soil one last time. This will remove any weeds and will loosen the soil and allow the plants to become established more quickly.

Read: How To Grow Vegetables In Balcony.
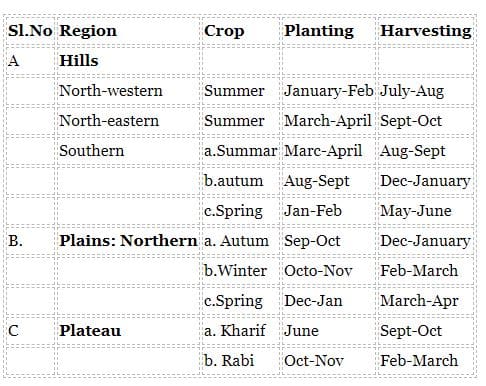
Planting and harvesting time for different regions of India:
Irrigation Requirement for Potato Crop:
Keep your potato vines well watered throughout the summer, especially during the period when the plants are flowering and immediately following the flowering stage. During this flowering period, the plants are creating their tubers and steady water supply is crucial to good crop outcome.

Potatoes need consistent moisture, so water regularly when tubers start to form Potatoes do well with 1-2 inches of water or rain per week. When the foliage turns yellow and begins to die back, discontinue watering. This will help start curing the potatoes for harvest time. Drip irrigation helps Indian farmers increase potato yield.

Crop Rotation in Potato Crop Production:
Crop Rotation is very important in potato farming, so practice yearly crop rotation.
Common Pests and care in Potato Plantation:
- Aphids 2) Flea Beetles 3) Leaf Hoppers 4) Early/Late Blight 5)Potato Scab: Most likely caused by soil with high pH. Remember Potatoes like acidic soil (do not plant in soil with a pH higher than 5.2). Dust seed potatoes with sulfur before planting.
Manure application for Potato Plants:

Potatoes like a slightly acid soil, pH of around 5.0 but will grow in a range from 5.0 to 6.5. Common potato scab (brown corky tissue on the surface of tubers) can be a problem if the soil pH levels are on the alkaline or “sweet” side.
If you have access to animal manures, aged or composted manures are the best. Nutrient quality and quantities can vary a lot, with the age and storage method being two of the most important. No matter what the quality of the manure, there is still enormous value as far as providing the soil microbes with a material they need to build fertility.
Manures are best added to the soil in the fall before planting to allow the soil microbes time to do their magic, breaking it down into usable nutrients. Spread the manure over the garden before folding it into the top 6-8 inches (15-20 cm ) of soil with a plow, rotary tiller-hoe or shovel.
Harvesting Potatoes:

- Baby potatoes typically can be harvested 2-3 weeks after the plants have finished flowering. Gently dig around the plants to remove potatoes for fresh eating, being careful not to be too intrusive. Try to remove the biggest new potatoes and leave the smaller ones in place so they can continue to grow.
- The potato must be harvested at the right stage of maturity when leaves turn yellow and dry.
- If there is a demand in the market slightly early harvesting may be done.
- Irrigation is withheld before harvesting and harvesting is done when soil becomes dry.
- Cut the plants at ground level eight days prior to the date of harvesting.
- It is done with the help of kudali or potato digger or by plowing with deshi plow.
- Care should be taken to the dugout the tubers without injury.
- Collect the exposed tubers and cleaned off by removing soil, roots, stolons, etc.
- The damaged and diseased potatoes are sorted out and discarded.
- Remaining potatoes graded according to size and stored in shade to avoid sun injury.
- The diseases free, medium to big size potatoes are selected and stored separately for seed purpose.
The yield of Potatoes per Hectare:

- The yield of potato varies from a variety from variety season of planting and care taken during cultivation.
- The average yield of potato in Maharashtra is about 125 qt/ha.
- The average yield of potato in India is about 200 to 300 qt/ha.
Friends, that’s all about how you can grow potatoes on your own and keep growing vegetables for building a healthy world.







