Pathogen. The early blight fungus is found in most soils where potatoes are grown, and the disease develops every season. The fungus overwinters in the soil on dead leaves, vines or infected tubers.
Disease development. In the spring, the fungus produces spores on the infected crop residue. Spores are spread to healthy plants by wind and rain. Usually, older leaves close to the ground are infected first. Early blight is more severe as the potato crop ages or if the crop has been stressed by poor nutrition, drought, hail, insect damage or other stress. Plants infected with Verticillium or expressing common mosaic symptoms are particularly
susceptible to early blight.
If early blight is severe, lesions may also be found on stems and tubers. Tuber infection occurs at harvest primarily through cuts, bruises or wounds. The variety Nordonna is susceptible to tuber infection.

concentric rings that resemble a target board
occur on the leaves. Dead tissue usually
collapses, leaving a hole.

by large leaf veins and surrounded by
a yellowish area.

Early blight lesions are not limited by small leaf
veins.



infection is severe.

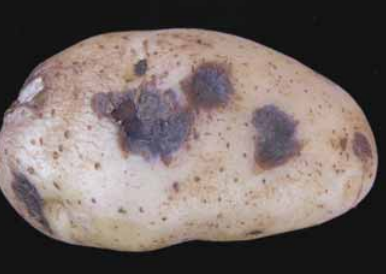
slightly sunken, and round to irregular in shape.
The lesions are often surrounded by a raised,
violet-blue border.

brown, dry and corky. If the infection is shallow,
the rotten tissue can be easily removed. Tuber
symptoms appear in storage.










